Establishment of a standardised and integrated data platform for TEG (Ticketek)
8 minute read
24 October 2025

Through their integrated operating model, TEG (Ticketek) bring the best live content, ticketing and technology to their partners and create memories for fans that last a lifetime. A key differentiator in their approach is being a truly digital company first, enabling data and analytics to help shape the customer experience.
“One of the best technology partnerships I have been involved in. A game-changing result for TEG’s global operations.”
- Andrew Reid
General Manager, TEG Ovation
In this multi-part series, we’ll explore how TEG and Altis built a modern data platform for ingesting streaming data into Snowflake, integrating with the Braze customer engagement platform and automating solution deployments globally.
Part 1: Data platform
Objectives
TEG sought to rationalise their existing technology stack and provide a foundation for unifying and sharing data across the enterprise, capable of satisfying various business use cases.
AWS and Snowflake provide scalable services to support lowlatency data ingestion into the platform.
The consolidated and shared data capability was initially proven by developing a two-way integration with the Braze customer engagement platform. Braze enables TEG to deliver cutting-edge digital marketing to customers.
In support of TEG’s continued global expansion, the platform was designed with automated deployment processes including Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and Continuous Integration / Continuous Deployment (CI/CD).
High Level Architecture
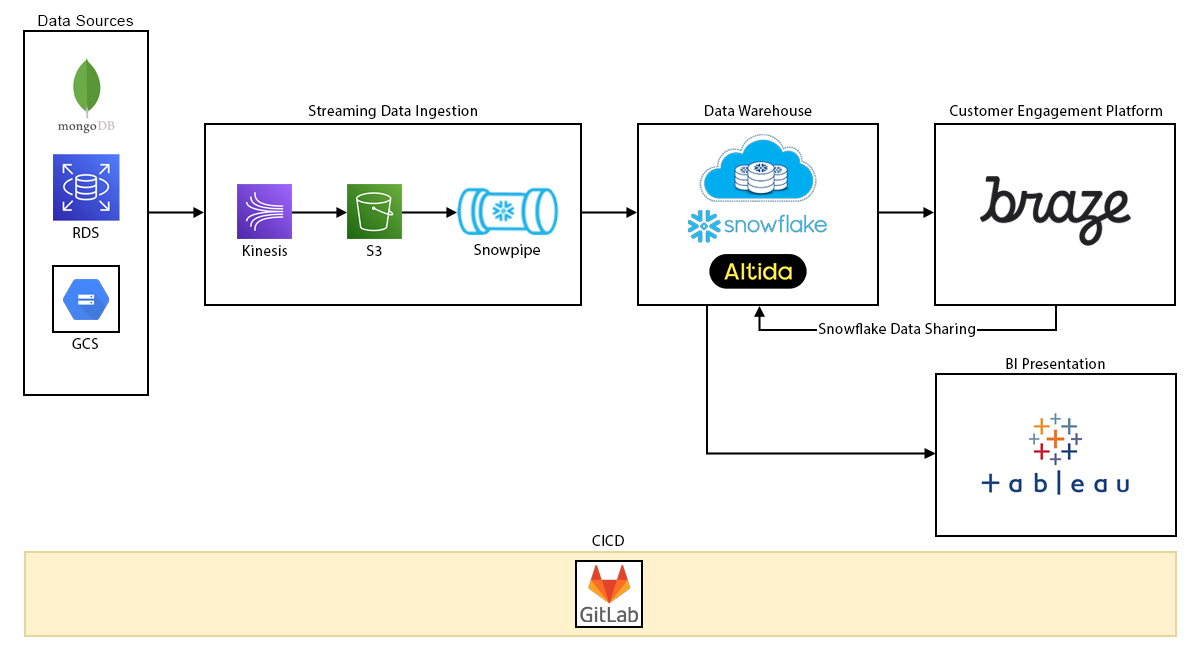
Streaming data ingestion is achieved using AWS cloud services including RDS, Kinesis & S3 together with Snowflake features such as Snowpipe, streams and tasks. Auxiliary data sets from TEG’s analytics business unit (Big Query / Google Cloud Storage) are also ingested into Snowflake, further enriching existing customer data.
Altis' Altida Data Load Accelerator (DLA) was implemented to expedite development of the Snowflake staging and presentation layers through its’ feature-rich and metadata driven approach. This framework gives the data platform the ability to be easily extended in future.
Both streaming and batch data pipelines are supported via the Braze “user track” and “subscription status” APIs. Snowflake data sharing is utilised to surface Braze data within TEG’s own Snowflake environment.
Business users can access operational reporting and analytics via Tableau connected to Snowflake.
Gitlab CICD pipelines and a structured approach to developing additional features enables the data platform to be rolled out to TEG’s global regions in a consistent manner.
Why TEG Chose Altis
Altis Consulting has a proven track record in designing and implementing modern data platforms. Altis is used to delivering large programs of work that span platform migration, business requirements gathering and end-to-end solution delivery.
“A massive achievement for TEG in our progression to be a data-driven enterprise.”
Tane Oakes
Chief Technology Officer, TEG
Part 2: Data ingestion
In this part of the series, we’ll explore how Altis and TEG achieved real time data ingestion into the data platform using AWS and Snowflake components.
Altis supplied two metadata driven frameworks to simplify and expedite the development process:
- Snowstream: for streaming operational data into Snowflake staging
- Altida Data Load Accelerator (DLA): for populating the data warehouse dimensional model
Each section of the data ingestion solution are discussed in more detail below.
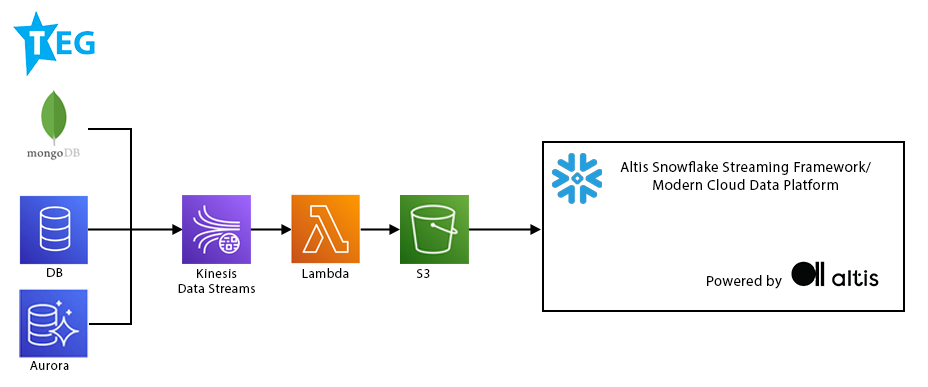
Source System to Cloud Storage
AWS Kinesis & Lambda are used to process and transform source system data, making it available in Simple Storage Service (S3) before it is ingested into Snowflake.
Each logical streaming object has an individual instance of these products to maximise performance and scalability. Read more about this in the following case study.
Cloud Storage to Snowflake Staging
Altis Snowstream is a purpose-built tool for ingesting and integrating streaming data into Snowflake with CICD support. The tool is built using native Snowflake SQL components requiring no additional software. Watch a 35-minute webinar on Snowstream here. Snowstream provides a repeatable pattern to accelerate the development process. It is a metadata driven approach and ensures the platform can be supported with minimal skills.
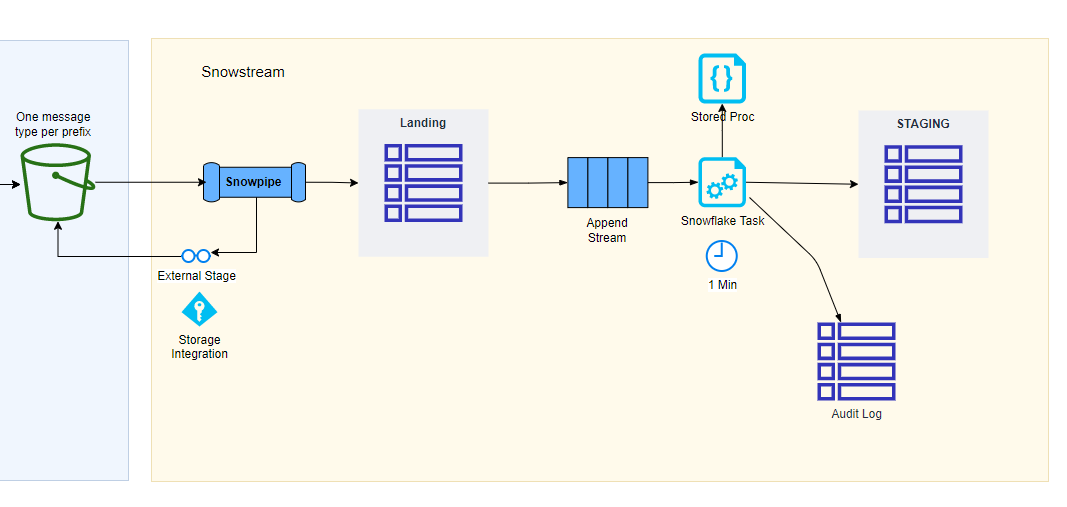
The following is a summary of the Snowflake components used by Snowstream and a high-level description of their purpose:
- Storage Integration: Provides a secure connection between Snowflake and AWS S3
- External Stage: JSON files for each object in S3 are referenced via a Snowflake external stage.
- Snowpipe: When objects are created in S3, event notifications trigger Snowpipe to execute a copy command from the external stage to a landing table.
- Table streams: Simplifies how new data in landing is detected (change data capture)
- Tables:
- Object definition metadata is stored in standard database tables. Both simple and complex JSON
(e.g., multiple nested arrays) can be accommodated. Several load patterns (e.g., append, merge)
are supported. - Audit Log tables record processing activity
- Object definition metadata is stored in standard database tables. Both simple and complex JSON
- Stored Procedures: SQL code that can be called to process data from landing to staging schemas according to the metadata definition.
- Tasks: Execute SQL on a schedule. Can be configured to only execute if streams have data. Tasks can be chained together to aid data processing orchestration.
Snowflake Staging to Presentation
After operational data has been streamed into Snowflake staging, the Altida DLA framework is used to control the flow and transformation of data into a dimensional model. This presentation layer is accessed by the BI tool (Tableau) where reports and dashboards are served to TEG’s business users.
Altida provides pre-built logic and data orchestration templates to reduce development time and allow developers to focus on value adding business requirements.
The process is orchestrated using Snowflake tasks which call SQL stored procedures. Altida stored procedures reference SQL views which contain the data transformation business logic and populate the data warehouse star schema.
Part 3: Braze integration
In this part of the series, we will explore how Altis, and TEG established a near real-time data integration with the Braze customer engagement platform.
TEG uses Braze to provide meaningful, personalised campaigns to customers. The Snowflake data platform described in previous parts of this series provides a powerful source of data to customise and trigger campaigns in Braze.
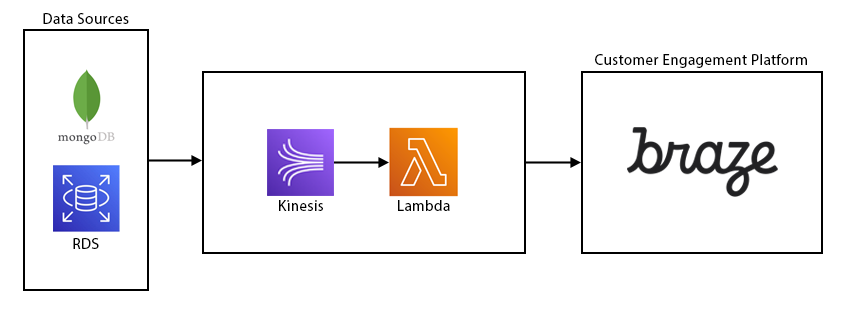
Architecture
The data integration from TEG’s ticketing platform to Braze uses lambda architecture to support real-time streaming and batch processes. A combination of AWS and Snowflake services were utilised to achieve the lambda architecture.
An important architectural consideration is the use of AWS serverless features. This allows the solution to scale out during periods of high volume and scale in during quiet periods.
Snowflake tasks were used for batch orchestration and external functions for the API integration with Braze. The batch processing component is also used for historical data migration when initially loading data into Braze as well as regular data reconciliation between Snowflake (source of truth) and Braze to ensure data synchronisation. Batch was also useful to ingest the Data Science calculations such customer segments. Braze supports data sharing through Snowflake which provides an easy-to-setup and seamless connection between TEG’s own Snowflake data platform and their data in Braze.
Technical highlights
Some data sources used in the integration are SQL server, MongoDB, AWS Aurora. DB events from these sources were fed into a Kinesis stream for real-time processing.
Altis utilised the Serverless framework, automated testing, and DevOps approach to expedite development of the Lambda functions to process data in Kinesis streams.
Redis cache was used to provide synchronisation when joining streams and to cache reference data lookups.
The solution design incorporated monitoring, throttling and error handling controls between TEG and Braze. This is important to ensure TEG complies with the Braze API rate limits.
Part 4: DevOps
TEG are expanding globally and required an efficient and reliable process for rolling out their data platform solution into new regions. In this part of the series, we’ll explore how Altis and TEG built effective and robust Continuous Integration / Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) practices to facilitate this.
Source control
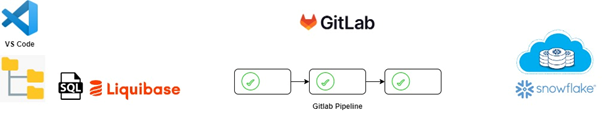
TEG uses Gitlab for their code repositories & source control. New repos were created for the various components of the data platform solution. This allows for fine grained control of the permissions granted to developers working on different parts of the solution. Gitlab pipelines and runners play an important part of the CI/CD process. Pipelines are written in YAML and contain the jobs, steps and commands associated with the deployment of a solution component.
Gitlab runners provide the compute power to execute the pipelines. The Gitlab UI provides a front-end for engineers to do required configuration changes at deployment time (e.g., specifying the target deployment region) and to monitor pipeline executions.
Pipeline execution works in conjunction with the Git branching strategy. For example, an approved merge request to the develop branch would trigger a pipeline run for the development environment.
Database Schema Management
Altis leveraged an open-source tool called Liquibase to track, version and deploy database changes to Snowflake. Data engineers used VSCode integrated with Gitlab to manage the SQL code.
The SQL files are named and stored in a thought-out folder structure to provide easy navigation of the solution. Liquibase requires the developer to use ‘changesets’ to organise the code into executable blocks which are tracked during each ‘liquibase update’ command. Liquibase maintains changelog tables in Snowflake to keep track of changeset deployments and modifications. Changesets give the developer the freedom to allow control over some SQL being executed once-off (e.g., table creation) versus some SQL being re-runnable if a change is detected (e.g. CREATE or ALTER VIEW…)
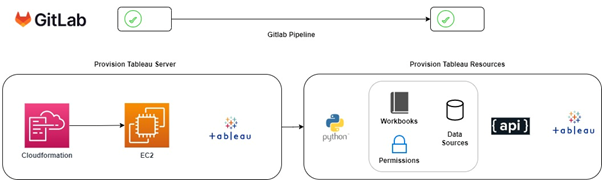
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
AWS Cloudformation templates were used to provision several AWS resources such as S3 buckets, IAM roles, SQS Queues, Lambda functions etc.
A noteworthy example of a solution component being automated is that of the Tableau server deployment. Cloudformation was used to provision the EC2 instance for Tableau server. Python scripts were used to call the Tableau server REST API in order to provision resources such as projects, permissions, data sources, workbooks etc. A master template of Tableau resources was defined in JSON and ensured that a consistent Tableau environment and user experience was rolled out for each region.
Ready to unlock the full potential of your data?
Partner with Altis Consulting to design and deliver modern, scalable data platforms that drive business performance and customer engagement. Contact us today to get the conversation started.
Meet the Team
Contributor
Share
Other insights
Contact us via the form on our website or connect with us on LinkedIn to explore the best solution for your business.